Feed-forward & feedback synthesis with prescribed controller structures
This example illustrates the design of a conventional 2-DOF control structure with restricted complexity of components.
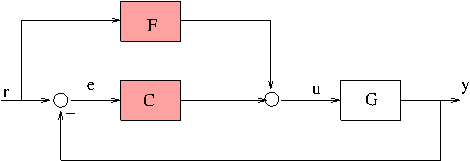
- The feedback component consists of a PID controller.
- The feed-forward block is a 2nd-order filter.
Contents
Define nominal plant
s = tf('s'); ny = 1; nu = 1; G = ss( 1/(s-1) ); % unstable SISO plant
Build synthesis interconnection and define specifications using linlft
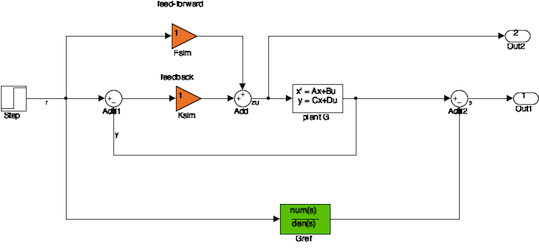
Define reference model capturing performance constraints.
num = 11.11; den = [1 6 11.11] ; Gref = tf(num , den); % reference model io = getlinio('TwoDOF'); % r, zu, e and y Blocks = {'TwoDOF/Ksim','TwoDOF/Fsim'}; Pperf = linlft('TwoDOF',io([1 3]),Blocks); % r -> e perf Pu = linlft('TwoDOF',io([1 2]),Blocks); % penalize control signal Psim = linlft('TwoDOF',io([1 4]),Blocks); % simulation channel
Define controller blocks
K = ltiblock.pid('K','pid'); % PID feedback F = ltiblock.ss('F',2, nu, ny ); % feed-forward of order 2 C0 = blkdiag(K,F); % gather all blocks
Include weighting functions and aggregate objectives
W1 = (0.25*s+0.6)/(s+0.006); % performance in the low frequency range Wu = 0.01 ; % control signal penalization % Gather closed-loop objectives through diagonal augmentation CL0 = blkdiag( W1*lft(Pperf, C0), Wu*lft(Pu,C0) ) ;
Run hinfstruct
[CL,gam] = hinfstruct(CL0);
Final: Peak gain = 0.0177, Iterations = 83
Retrieve feedback and feed-forward blocks in transfer function format
Kpid = pid(CL.Blocks.K), Ftf = tf(CL.Blocks.F),
Continuous-time PIDF controller in parallel form:
1 s
Kp + Ki * --- + Kd * --------
s Tf*s+1
With Kp = 3.05, Ki = 2.8, Kd = 167, Tf = 2.03e+05
Transfer function:
-3.763 s^2 - 24.35 s - 56.19
----------------------------
s^2 + 13.82 s + 22.81
Check results
norm( ss(CL) , inf), gam,
ans =
0.0176
gam =
0.0177
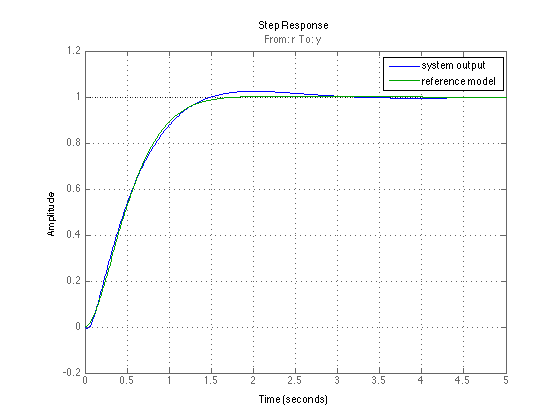
Simulate set-point responses
CLsim = lft(Psim, blkdiag(Kpid,Ftf) ); figure(8); clf; step(CLsim , 5); grid; hold on; step(Gref,5); legend('system output', 'reference model') ;